- Home
- Our Services
CANCERS WE TREAT
TREATMENT OPTIONS
- About Us
About North Houston
Cancer ClinicsNorth Houston Cancer Clinics is a leading cancer center specializing in treating various types of cancers and blood disorders.Meet our specialized cancer care team
Choosing excellence, transforming cancer care together
Quality Oncology Practice Initiative (QOPI) Certification Program
Discover Our Healing Spaces: Virtual Office TourFirst day visit at North Houston Cancer Clinics
Real Stories, Inspiring Journeys, Patient Testimonies
- New patient
Becoming a patient at North Houston Clinics
Embark on your journey to health with us. Seamless, compassionate care awaits as you become a patient at North Houston Clinics.
Effortless Registration, Portal to Wellness JourneyYour Health, Your Time, Your AppointmentFrequently Asked Questions For New Patients - Blogs
- Contact Us
- Home
- Our Services
CANCERS WE TREAT
TREATMENT OPTIONS
- About Us
About North Houston
Cancer ClinicsNorth Houston Cancer Clinics is a leading cancer center specializing in treating various types of cancers and blood disorders.Meet our specialized cancer care team
Choosing excellence, transforming cancer care together
Quality Oncology Practice Initiative (QOPI) Certification Program
Discover Our Healing Spaces: Virtual Office TourFirst day visit at North Houston Cancer Clinics
Real Stories, Inspiring Journeys, Patient Testimonies
- New patient
Becoming a patient at North Houston Clinics
Embark on your journey to health with us. Seamless, compassionate care awaits as you become a patient at North Houston Clinics.
Effortless Registration, Portal to Wellness JourneyYour Health, Your Time, Your AppointmentFrequently Asked Questions For New Patients - Blogs
- Contact Us
Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI Scans
North Houston Cancer Clinics offers all the advanced treatment and diagnostic plans for diagnosing cancer. Early cancer detection is critical in providing the best and most effective treatment. In MRI, specialists use magnetic solid waves to scan the organs and parts, which will show all the angles to detect cancer and tumors. Sometimes, people call these scans nuclear scans or magnetic scans. This MRI is a valuable tool in detecting cancer at its early stages.
Basic Understanding of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Size and presence of the tumor cells in the body
- To check about the stage and spread of cancer
- To check about the stage and spread of cancer
Facts About Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique
The following are some facts that one should know before taking the test.
1. You should not take your credit cards or other personal items with you while in the laboratory for this test.
In MRI, you are not exposed to direct radiation; instead, you experience strong magnetic waves that create images.
MRI is not allowed during pregnancy as it causes trouble and affects the baby and mother’s health. It is not prescribed to be performed during at least the first 13 weeks of pregnancy until or unless there is a serious problem.
People who are obese or have greater weight are having trouble getting fit into the machine.

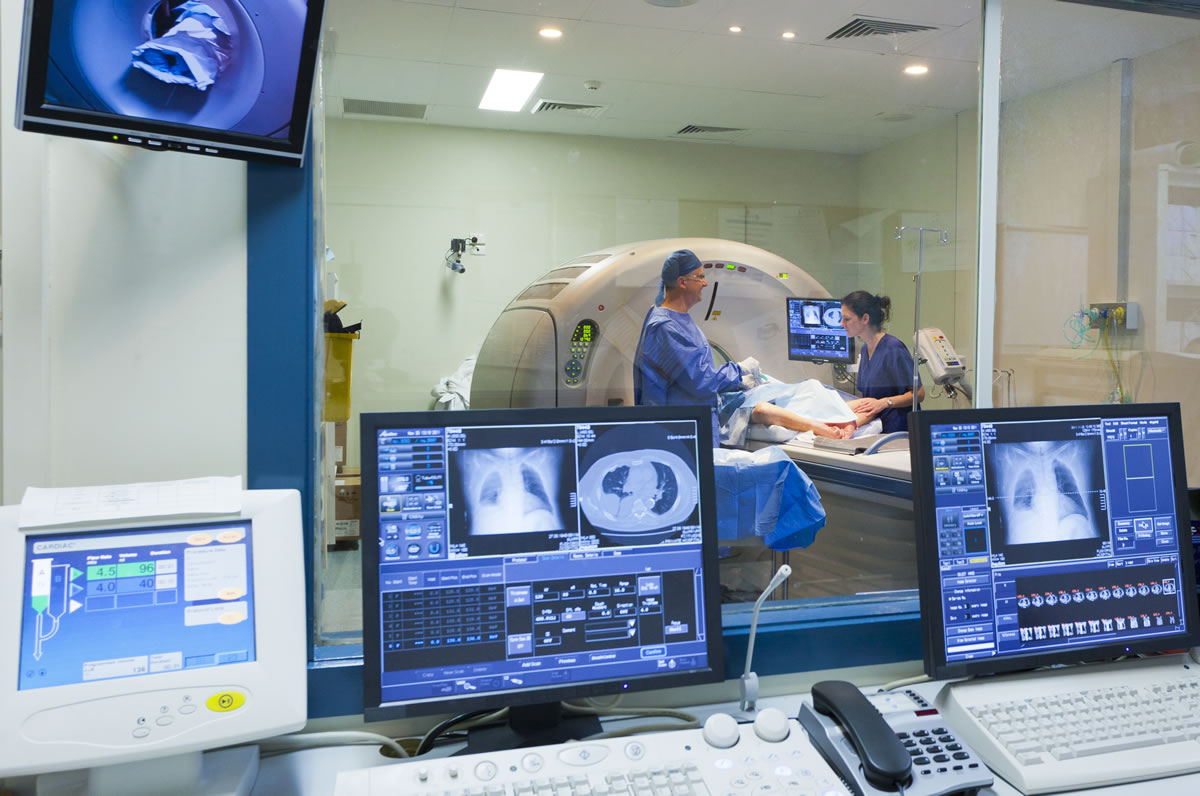
Computer Processing
Contrast Agents
Working and Role of MRI in Detection of Cancer

Detection of Tumor Localization
- Staging: Staging cancer means checking the spread and presence of a disease, and MRI is essential in such cases. By checking for involvement from surrounding cells, oncologists utilize MRI when choosing appropriate treatment options.
- Monitoring: MRI monitors the response to cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Follow-up MRI scans can assess changes in tumor size and appearance, helping clinicians evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Needle Biopsy:Needle biopsy is a diagnostic method used to detect cancer and body tumors by guided needle biopsy.
- Minimizing Unnecessary Tests:By identifying evidence pointing toward cancer soon via physical examinations, we frequently reduce invasive and costly diagnostic tests.
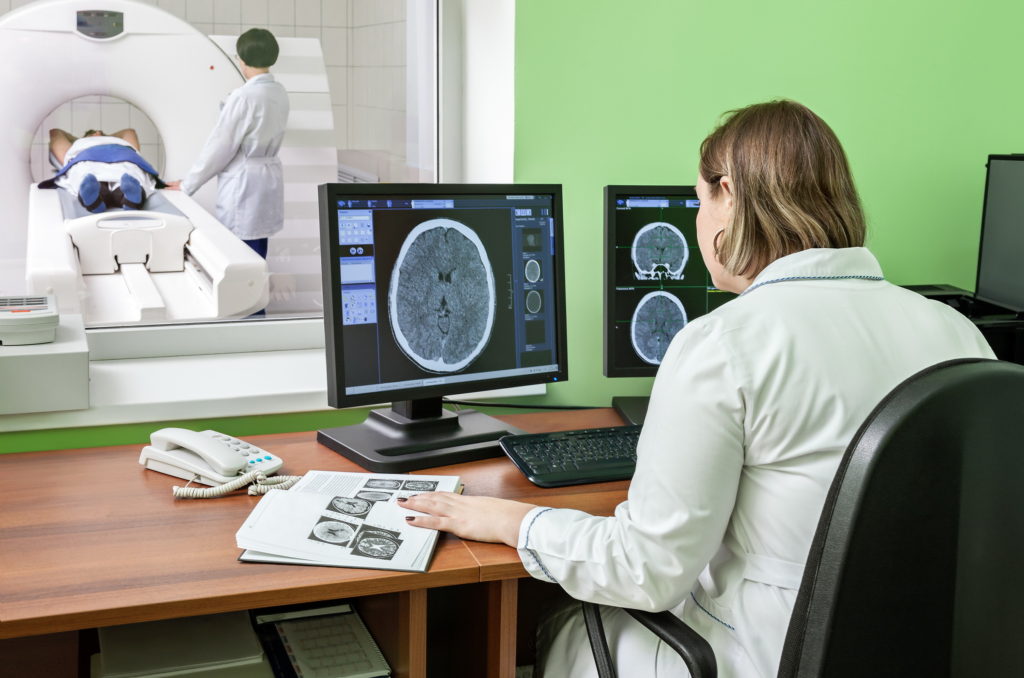
What happens in this test
The MRI process starts by getting the patient ready by removing their jewelry and other items they are wearing. Patients have to change their clothes into a gown or something loose.
A dye called contrast medium is given to the patient, which helps enhance the part that needs to be considered. This dye is injected through an intravenous route. Some people feel pain or disturbance in the stomach.
When the scan starts, you will lie on the back of the table. Every session will take 30 minutes in about 2-5 series.
Challenges and Future Directions
This imaging technique is beneficial and has some points to consider when performing MRI scans. You need to ask some related questions, including the MRI duration and working and who will perform your MRI—other risk factors related to the occurrence of MRI, and if any other tests and reports are required. It would help to ask about the cancer clinic’s cost and other related information before this test happens.
However, despite these limitations, ongoing research and technological advancements continue to enhance its role in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Such advances include new types like molecular imaging and functional Magnetic resonance imaging, which promise improved accuracy and specificity in diagnosing cancer.
