Cancer Screening
Cancer screening week is from December 4th to December 8th
Breast cancer screening
Invasive female breast cancer incidence rates have been increasing by about 0.5% per year since the mid-2000s. Getting screened regularly is the most reliable way to find it when it’s smaller and might be easier to treat. In fact, breast cancer death rates have been declining since 1989 due in part to screening with mammograms as well as increased breast cancer awareness and improved treatment. Women at high risk are those with a personal history or strong family history of breast cancer, a genetic mutation known to increase risk and those had high-dose radiation therapy to the chest before age 30 Women at average risk should have the option to start screening at age 40 with a mammogram every year. Women ages 45 to 54 should get a mammogram every year. At age 55 and older, women can switch to a mammogram every 2 years or continue annual screening. Screening should continue for as long as a woman is in good health and expected to live at least 10 more years
Breast cancer screening
Invasive female breast cancer incidence rates have been increasing by about 0.5% per year since the mid-2000s. Getting screened regularly is the most reliable way to find it when it’s smaller and might be easier to treat. In fact, breast cancer death rates have been declining since 1989 due in part to screening with mammograms as well as increased breast cancer awareness and improved treatment. Women at high risk are those with a personal history or strong family history of breast cancer, a genetic mutation known to increase risk and those had high-dose radiation therapy to the chest before age 30 Women at average risk should have the option to start screening at age 40 with a mammogram every year. Women ages 45 to 54 should get a mammogram every year. At age 55 and older, women can switch to a mammogram every 2 years or continue annual screening. Screening should continue for as long as a woman is in good health and expected to live at least 10 more years

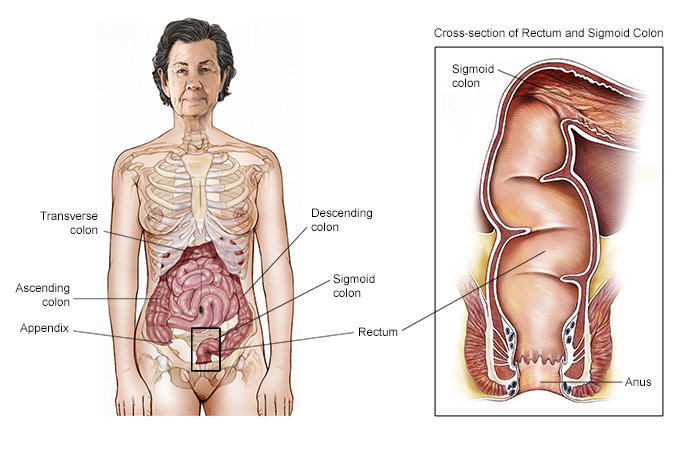
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer is cancer that occurs in the colon or rectum. It doesn’t always cause symptoms, especially in early stages. But with regular screening, it can often be prevented or found early when it’s small and might be easier to treat. People at high risk include those with a personal history of colorectal cancer and certain types of polyps, a family history of colorectal cancer, a personal history of inflammatory bowel disease, an inherited colorectal cancer syndrome and a personal history of getting radiation to the abdomen or pelvis.
There are several effective tests available, including visual tests (colonoscopy, CT colonography and flexible sigmoidoscopy) and at-home stool tests that look for abnormal fecal DNA or blood. Stool-based tests include a highly sensitive fecal immunochemical test (FIT) every year, a highly sensitive guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT) every year, and a multi-targeted stool DNA test (MT-sDNA every 3 years) Visual exams include a colonoscopy every 10 years, CT (virtual colonoscopy) colonography every 5 years, and a flexible sigmoidoscopy every 5 years If a person chooses to be screened with a test other than colonoscopy, any abnormal test result should be followed up with colonoscopy.
