Prostate Cancer
What Is Prostate Cancer ?
Prostate cancer usually develops slowly and has no symptoms in the early stages. However, as the cancer progresses, the symptoms include difficulty urinating, bleeding in the urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, pain in the pelvis, etc. It’s not very common, but in a few cases, the cancer in the prostate spreads to other parts of the body, which causes more severe symptoms and complications.
It is a common type of cancer found in males, but if early detection is possible, then the oncologist will identify them through prostate cancer diagnosis and start the treatment.
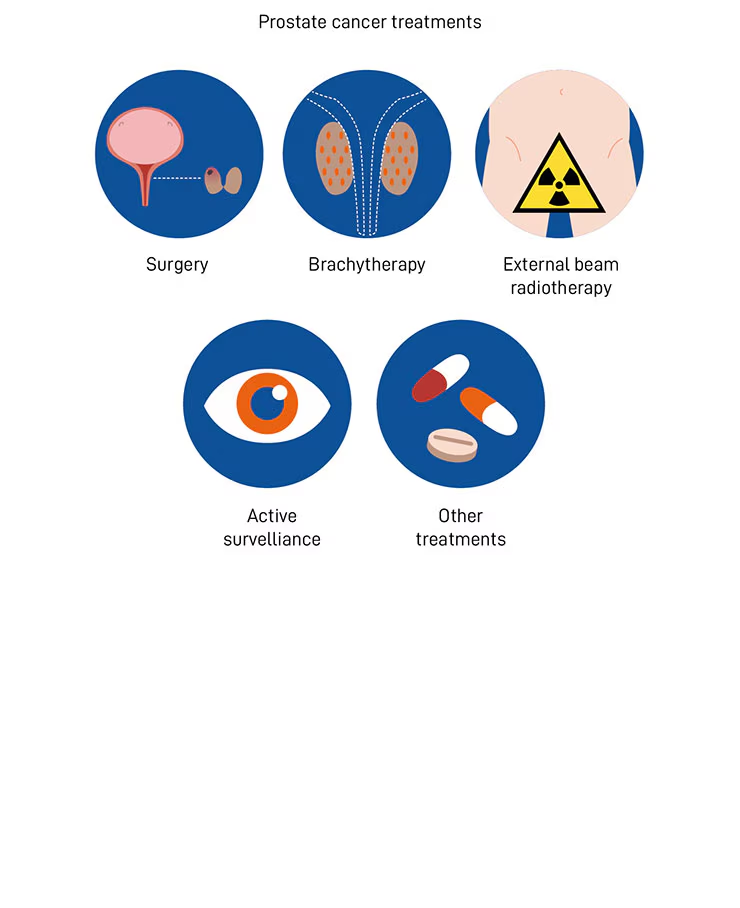
Prostate Cancer Treatments
The treatments for Prostate cancer depend on several factors, including the progression and aggressiveness of the tumor and the extent to which it spreads. It also depends upon the patient’s age and their health conditions.
Surgery
Surgery of the prostate is also called prostatectomy, which includes an operation in which the doctor removes the prostate gland of the patient. In some cases, seminal vesicles, along with the prostate gland, are removed. This specific gland is responsible for producing semen.
Radiation Therapy
In radiation therapy, high-energy waves are used to kill cancer cells present in the prostate.
Expected Management
There are some cases when doctors suggest patients not to start the treatment for the prostate gland as it is not growing. Instead of getting Prostate cancer treatment, doctors recommend them to monitor if any symptoms appear or not.
The diagnosis of prostate cancer generally consists of medical history, physical examination, blood tests (such as PSA tests), and imaging tests (such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans) Biopsy, . When a small prostate gland is removed and examined microscopically, it is usually necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
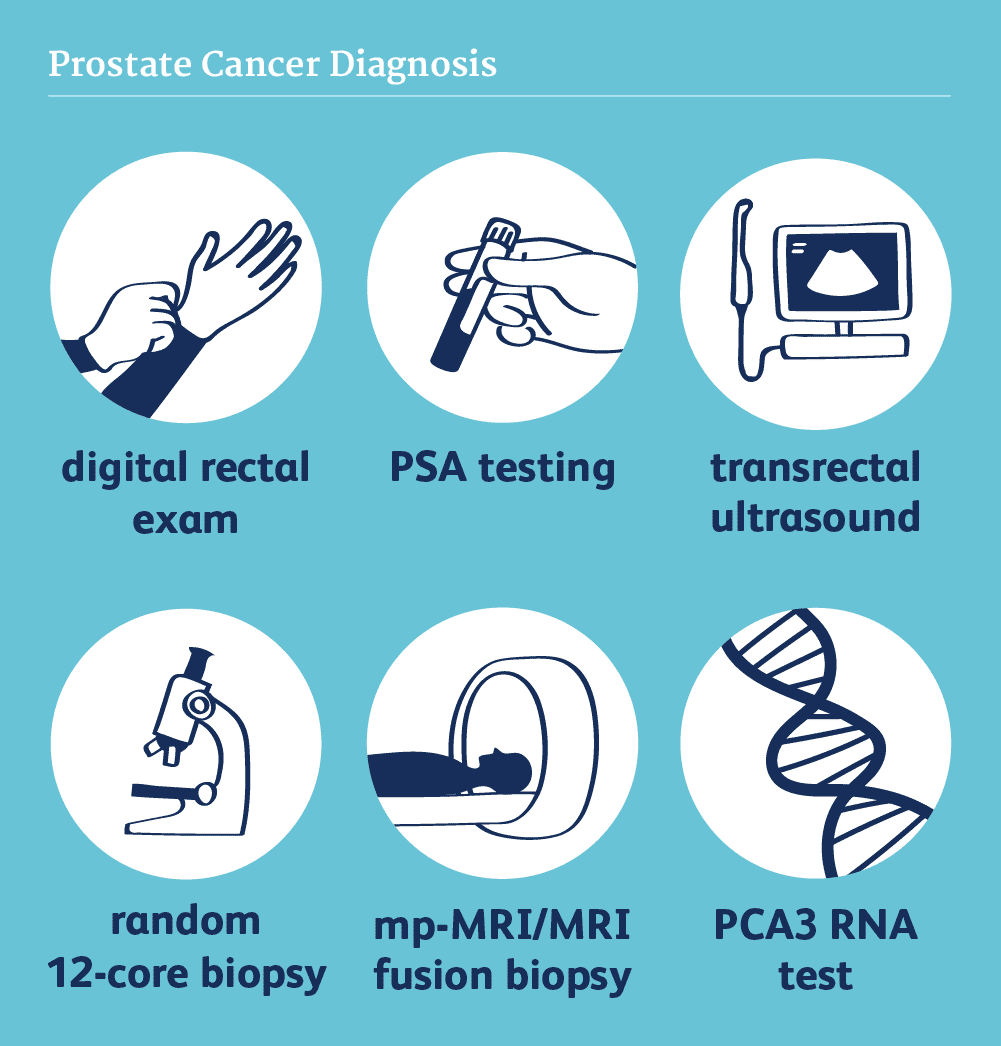
Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Prostate cancer diagnosis is a multifaceted process that involves different testing methods and techniques to determine the state of cancer in the prostate gland accurately. The diagnostic process aims at early identification of the disease when it can still be treated effectively. Essential elements of prostate cancer diagnosis encompass medical history assessment, physical examination, PSA test study, imaging studies, and biopsy.
Medical history evaluation: Physicians start by taking detailed histories from patients, including symptoms they may have experienced, past diseases or conditions, and family history of cancer, among other relevant details.
Physical examination: DRE- digital rectal examination is often performed during physical examination where a doctor inserts a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum and feels for any abnormalities like lumps or enlargement on the prostate gland.
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing: PSA is a protein made by the prostate gland, and increased levels found in blood could suggest
Imaging studies: Various imaging techniques, such as MRI scans, ultrasound, and CT scans, help visualize the condition of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues.
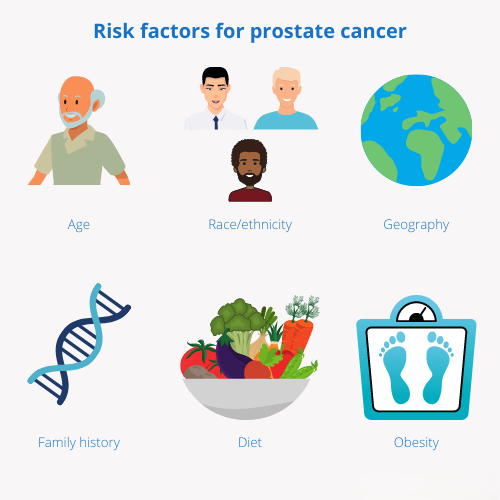
Causes and Risk Factors of Prostate Cancer
The following are some causes and risk factors related to prostate cancer.
- Age
Age is a leading factor as, most of the time, prostate cancer develops with the increase in age. After the age of 50 years, there is an excellent chance of developing prostate cancer.
- Genetics
Genetic mutations and having a history of prostate cancer play an important role in causing this cancer.BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are the most critical genes related to prostate cancer.
- Lifestyle Factors
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and having regular physical activity will help prevent cancer. Obesity or being overweight is also a risk factor associated with prostate cancer.
- Hormonal Imbalance
Having increased levels of testosterone may increase the chances of development of prostate cancer. Changes in the androgen receptors, which directly bind to testosterone, play a role in developing prostate cancer.
- Environmental Exposure
Environmental exposures include exposures from hazardous agents or rays, including cadmium, which may increase the chances of prostate cancer.
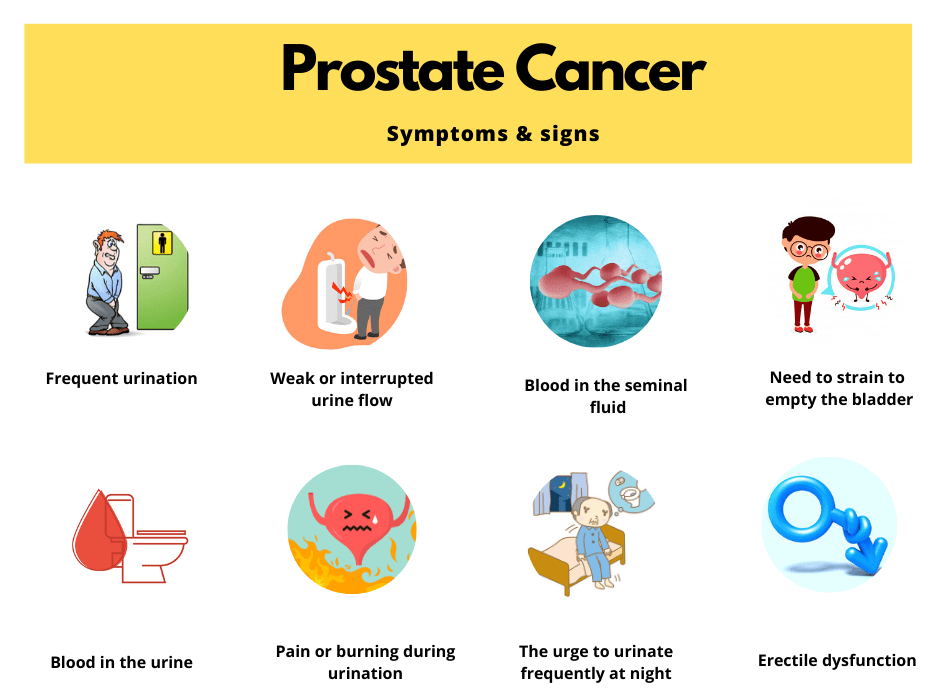
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Common symptoms of prostate cancer include itching and irritation in the urinary and genital regions. Sometimes, difficulty in urination and ejaculation occurs with painful urination. The patient will feel pain in the back and hip region. In advanced cases of prostate cancer, the cancer develops to a severe stage or when the prostate spreads to different areas of the body.
The patient will experience some severe symptoms that can be detected by prostate cancer diagnosis, including bleeding and frequent urge to urinate with weakness and unexplained weight loss.