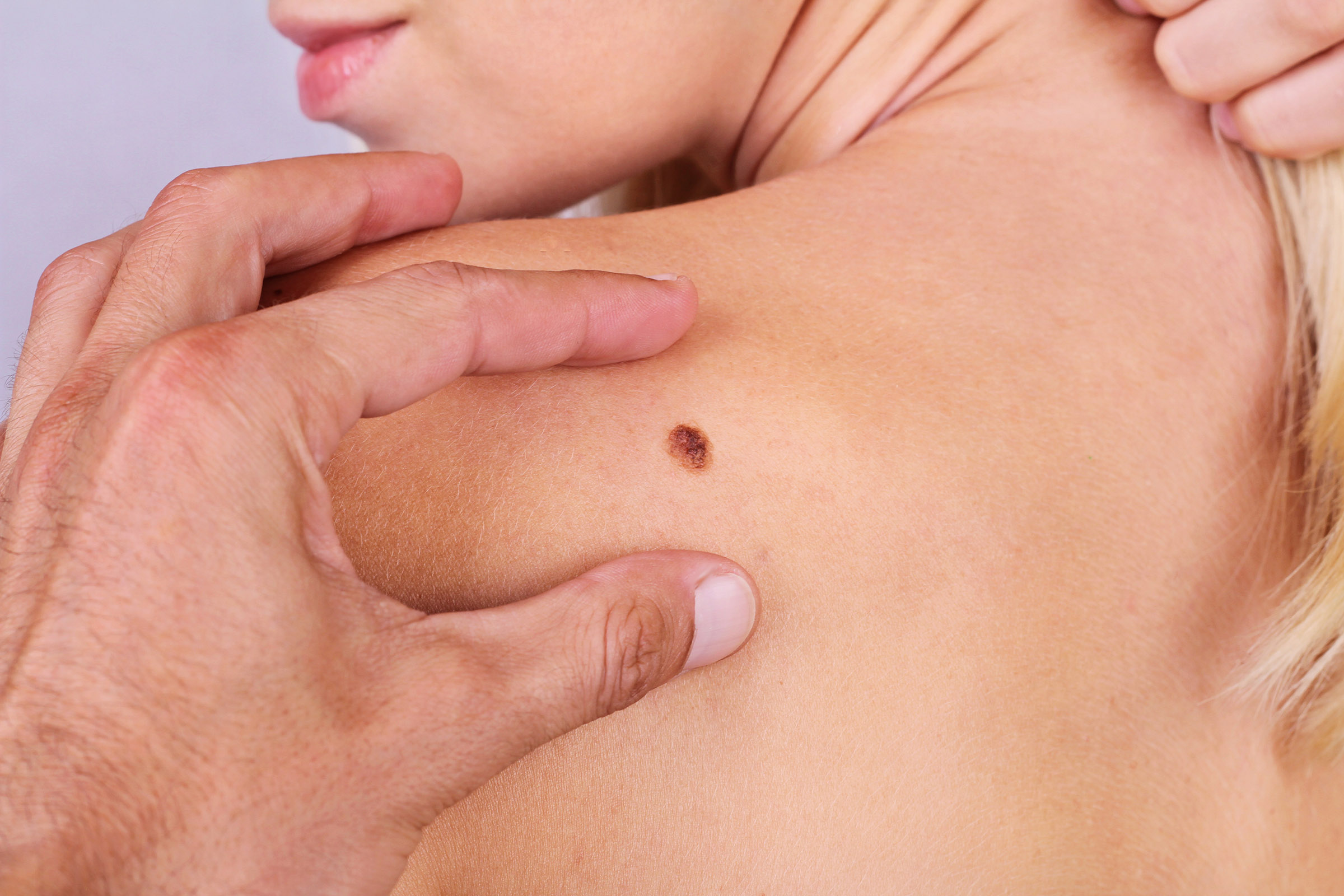
Skin Cancer
What is Skin Cancer ?
Skin cancer has become increasingly prevalent in recent years. The skin, the body’s largest organ, comprises numerous skin cells distributed throughout. Sunlight exposure is usually the primary cause of skin cancer, although people of all races and from various countries can develop it for different reasons.
Skin cancer can be categorized into three common types, including basal cell carcinoma(BCC), squamous cell carcinoma(SCC), and melanoma, each originating from different skin cells and exhibiting distinct characteristics. Nonmelanoma skin cancers are generally easier to treat and less likely to recur.
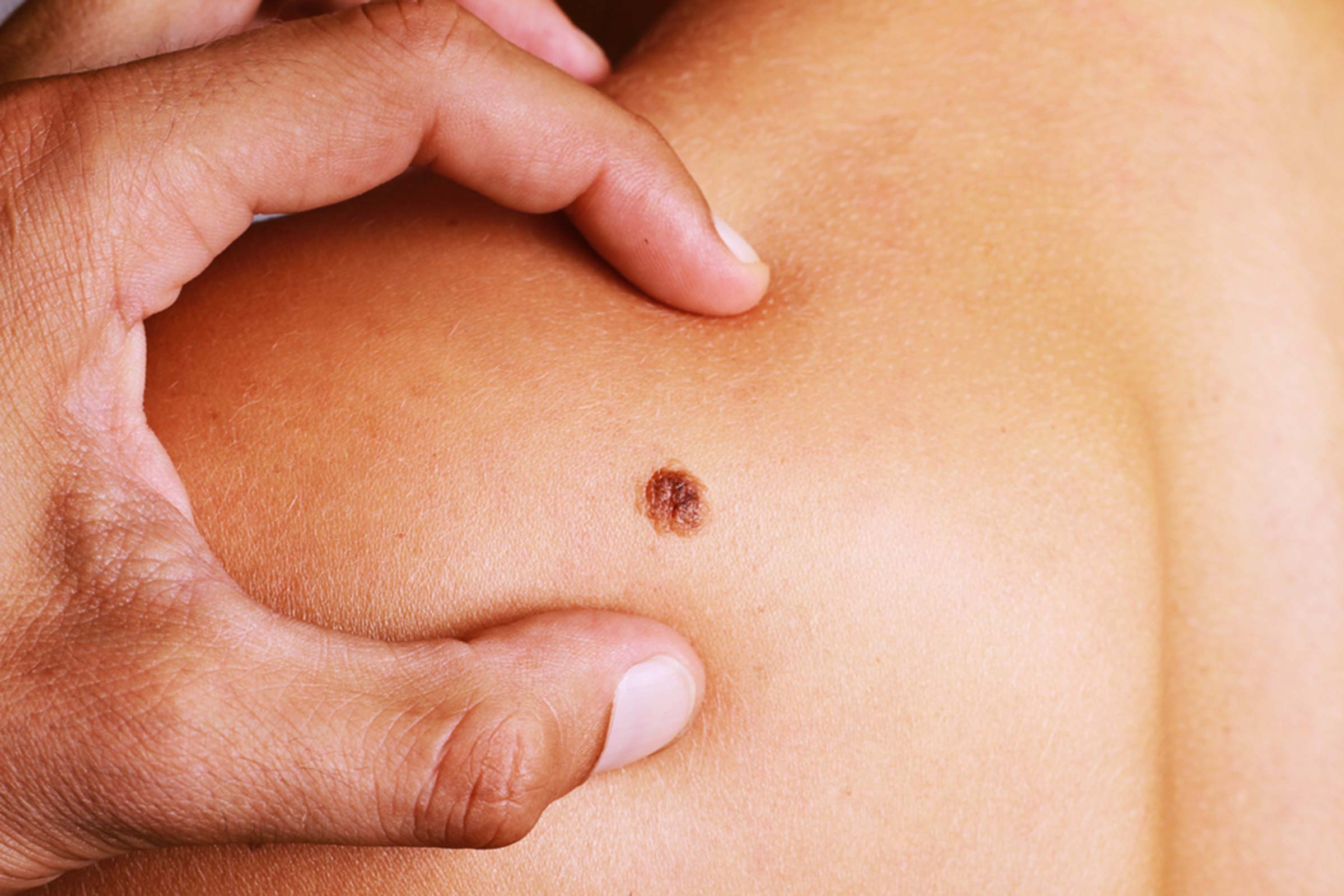
Skin Cancer Treatment Options
Skin cancer is treatable and can be treated through different options. Doctors start doing treatment by considering these factors :
- Type and stage of skin cancer
- Situation of patient
- Location of skin cancer
- Extent of Spread
Doctors and surgeons will discuss the type of treatment according to the patient.
- Radiotherapy: It includes treating cancer cells by using high-energy rays. Professionals will direct the rays toward the cancer cells and kill them. Radiotherapy also reduces the chances of reoccurrence of skin cancer.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment involves using the body’s immune system to kill cancer cells. Many immunotherapy creams and solutions are used.
3. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves killing cancer cells using anti-cancer drugs called cytotoxic drugs. Sometimes, a cream or intravenous injection will perform this work. Experts can use chemotherapy creams to treat severe skin cancers, including actinic keratosis and Bowen’s disease.
Skin Cancer Diagnosis
This is usually brought about by visual examination. Dermatologists usually make the diagnosis after examining the lesion or, if necessary, by performing a biopsy to confirm their diagnosis.
A biopsy is when the piece of skin lesion is viewed under a microscope. This is important in finding out the kind of skin cancer, and it is also very important in planning the treatment since it can determine the stage or spread of the disease.
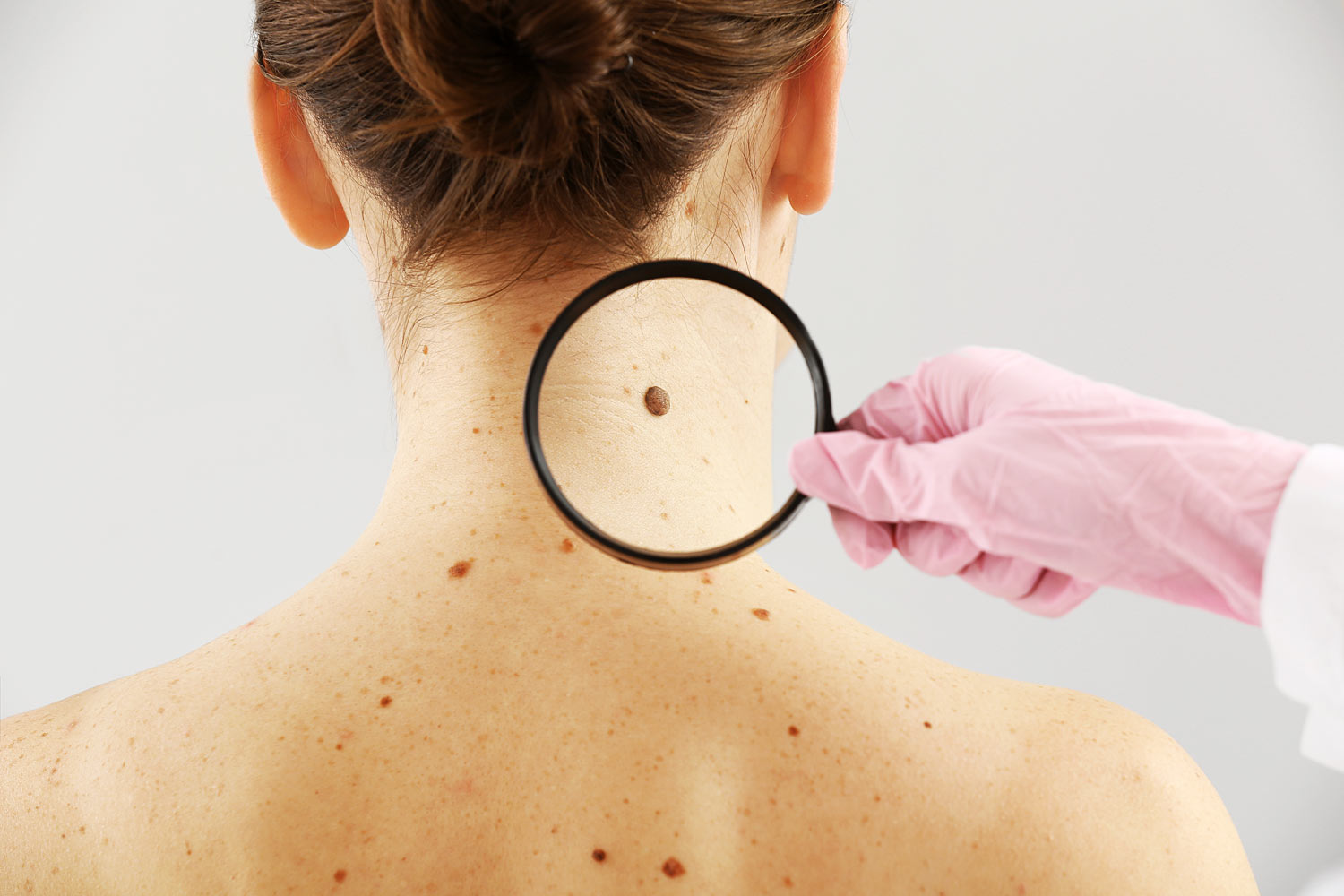
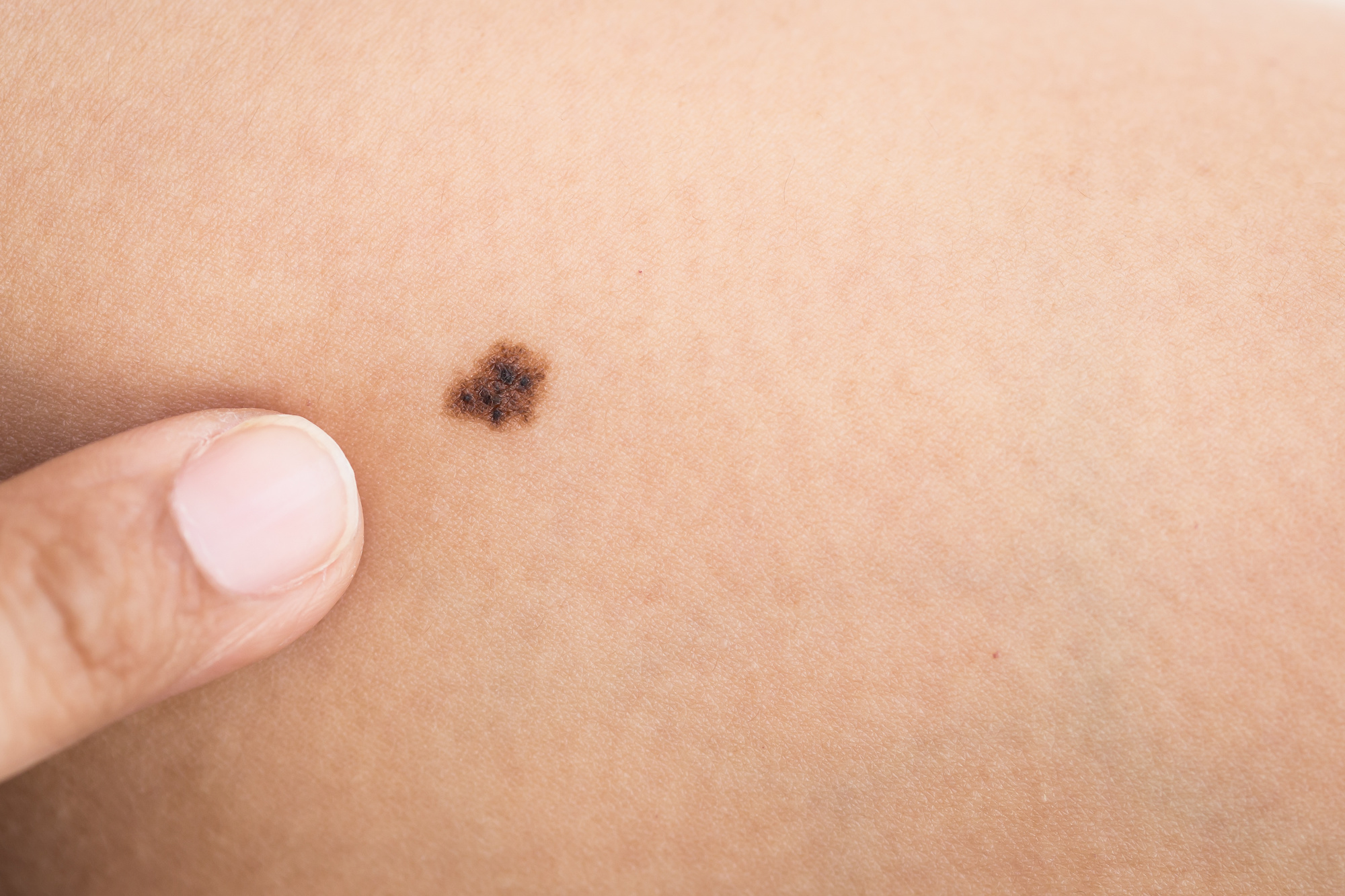
Types Of Skin Cancer
Some of the common include basal, squamous, and melanoma; all of these are different cells on the skin and thus differ from each other.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC):
Basal cell carcinoma develops in areas exposed to sunlight, but it can also occur in other parts of the body. Even though BCC’s behavior is very locally invasive, with slow growth and very little probability of distant site spread, it may still cause a significant amount of havoc by local invasion in surrounding tissues and invasion of underlying bones if left for some time without early treatment.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
It is named after the name of skin cells present in this area. People with lighter color tones have greater chances of squamous cell cancer. Parts of skin that are open to the sun, including the face, ears, nose, and other exposed areas, are more likely to get this cancer. Covered areas are comparatively safer than these parts. This cancer can develop in the genital areas of the body and also in scars and tissues.
- Melanoma:
Much more aggressive—almost reaching the point of being deadly—this type of skin cancer is much rarer. It begins in the melanocytes, cells that create the human protective melanin pigment responsible for body and skin pigmentation due to protection from ultraviolet rays. Melanoma is disposed to fast diffusion to other organs and tissues.
It can occur as a new, pigmented, spotty formation on the skin or in a pre-existing mole. Proper treatment and detection of the disease in time are of utmost importance since the chances of metastasis are inferior in melanoma.
Risks and Common Causes of Skin Cancer
Several factors and points cause skin cancer to occur, but the most common is exposure to sunlight. Nonmelanoma skin cancers are mainly caused by sun exposure.
- Sun Exposure
Sunlight plays a vital role in skin cancer as its exposure sometimes becomes fatal. Exposure can be long term or sometimes only a short period is enough. The rays damage the genetic material of the skin cells that mutate to form cancer cells.
- Sunbeds
People using sunbeds are developing skin cancers because research shows that sunbeds produce rays that damage the skin.
- Skin Color
Skin color is comparatively more likely to be involved in skin cancer. People with darker skin have high levels of melanin, a protective pigment used against skin cancer.