Throat Cancer
What is Throat Cancer ?
Throat Cancer Treatment Options
Radiation therapy is the solution you need. This stuff hits home! It has high-energy rays that do a great job at burning down those cells causing cancer in you, especially the ones given alone or with some other things, right? Below are the radiation therapy types for throat cancers:
External Beam Radiation Therapy: The beams come into the throat from the outside. It’s the most common one.
Brachytherapy: Have you ever planted seeds in the ground and then watched them grow? So we’re putting some radioactive seeds into those tissues to help them grow there instead.
Chemotherapy
They can work well on their own or combined with other forms of treatment, too! The following are chemotherapy agents used in treating throat carcinoma:
Cisplatin: A platinum-based chemo drug that makes it difficult for your tumor cells to survive.
5-Fluorouracil: Do not confuse it with something you eat! It is used along with cisplatin to treat throat cancer.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is much more precise than radiation or chemotherapy. Specificity helps, though! It employs medications designed to hit specific molecules involved in the growth of your tiny gremlin friends (cancer cells). We can still use targeted therapy alone or together in other ways:
Cetuximab: Other molecule targeting drug which kills it’s epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) this time around
Immunotherapy
It would be great to assist your immune system in identifying and attacking tumor cells. Let’s take some drugs; I’m sure that will make it happen sooner rather than later. Alone or combined, they could save you from these twisted cells:
Nivolumab: Drug targeting another molecule…this time it is programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)
Diagnosing Throat Cancer
Physical Evaluation:
Your local doctor would most likely want to perform a thorough check-up on your neck and throat to catch signs of cancer potentially.
Imaging Tests:
CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans are scans that commonly look for evidence of cancer in your throat. It also helps determine how severe your situation is.
Biopsy:
The only way to truly diagnose throat cancer is through a biopsy. A small sample from the throat is taken out and examined under a microscope for abnormal cells.
Endoscopy:
A small camera with a tube will be inserted to identify suspicious areas that could be places where growth is cited.

Recovery from Throat Cancer
Follow-Up Care: It’s important to have follow-up appointments with your doctor after treatment. They will help you recover and maybe even prevent cancer recurrence.
Supportive Care: Speech therapy and nutritional counseling may be offered to manage treatment side effects and improve quality of life.
Healthy Lifestyle: Eating good food, exercising, and avoiding tobacco/alcohol will help you live a great life. That’s not all, though. Those habits will also reduce your risk of developing throat cancer in the first place.
Risk Factors of Multiple Myeloma Cancer
Multiple myeloma diagnosis depends upon the factors and warning signs that cause this cancer. Following are some factors that increase the chances of multiple myeloma
- People older Than 50 are more likely to develop multiple myeloma. The chances of getting myeloma increase with age.
- Black people are more likely to get multiple myeloma than other people.
- Being male is also a significant factor in getting multiple myeloma.
- Inheritance also plays a significant role, and having a past family history of multiple myeloma will increase the risk of this cancer.
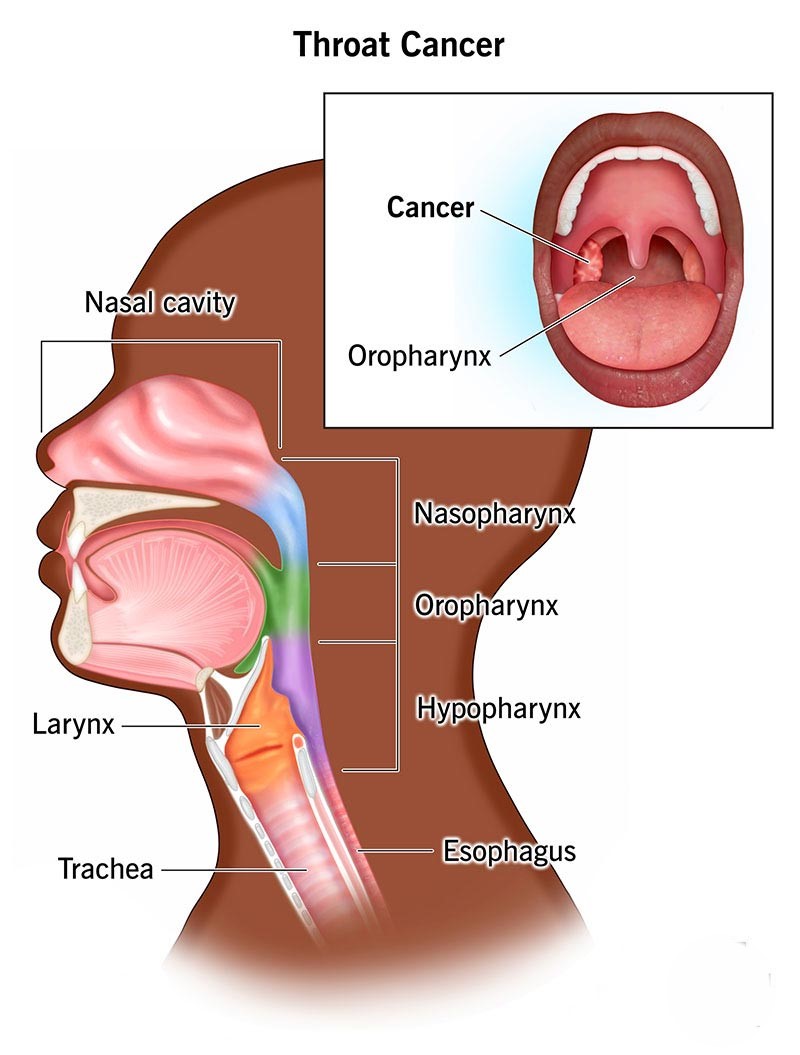
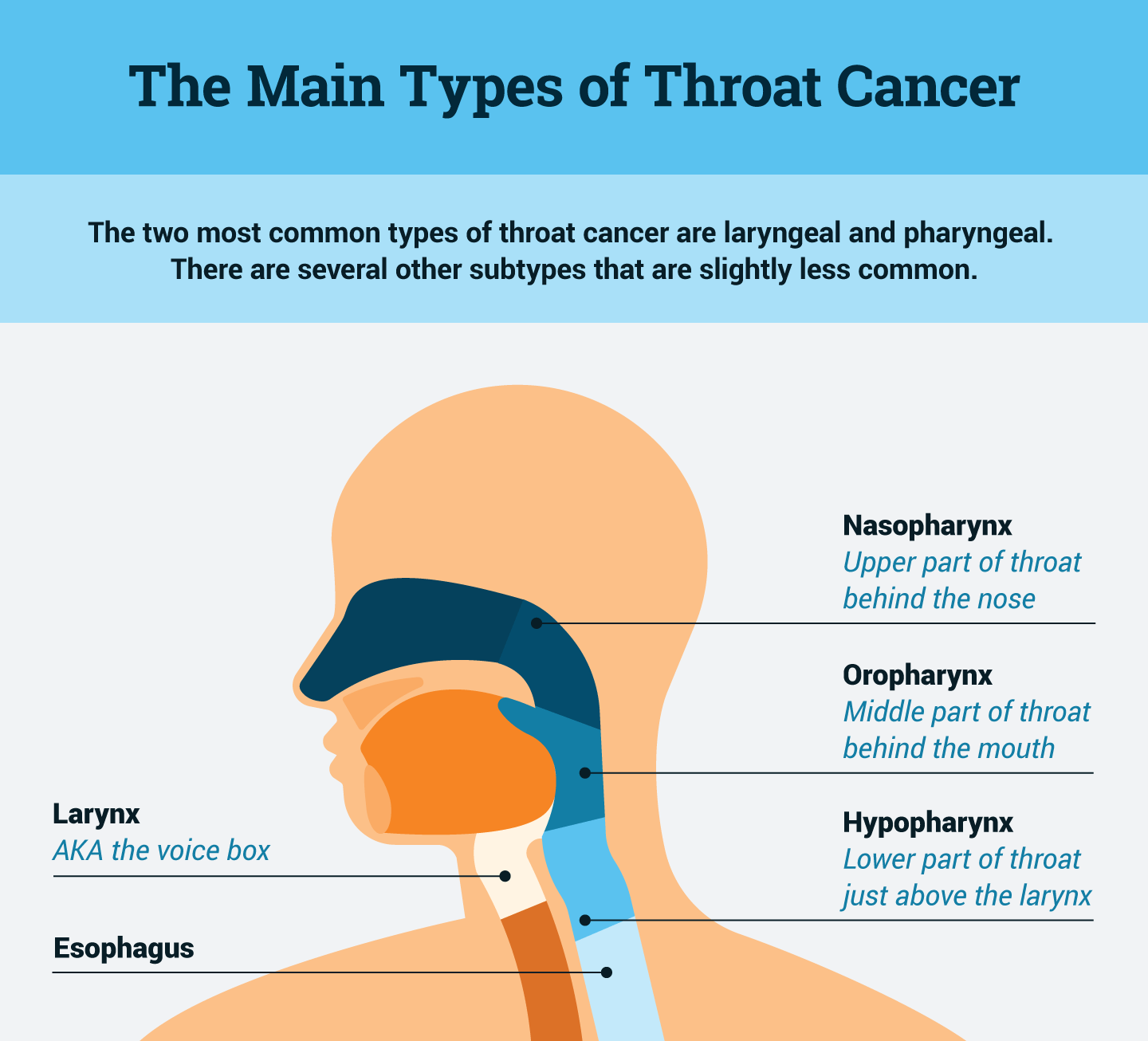
Types of Throat Cancer
Laryngeal Cancer:
It is a kind of throat cancer that affects the voice box or larynx. It is super common and often forms due to cell lining on vocal cords.
Pharyngeal Cancer:
This type targets the pharynx at the back of your nose and mouth. It usually begins in three specific sections: the nasopharynx (upper part of the throat), the oropharynx (middle part), or the hypopharynx (lower part).
Hypopharyngeal Cancer:
It is less common than any other form but worse when used because it is more aggressive. It mainly affects the lower throat, otherwise called the hypopharynx.

Symptoms for Throat Cancer
Persistent Hoarseness:
If hoarseness or changes in your tone persist for longer than two weeks, you should see a doctor about potential throat cancer.
Difficulty Swallowing:
Dysphagia is difficulty swallowing. If you have it, then you know it’s one annoying symptom. It’s generally seen in people suffering from this illness.
Ear Pain:
Doesn’t it ever go away? It might be a sign that you have ear pain, which could mean some growth in your throat is causing this issue.
Persistent Sore Throat:
Again, if it doesn’t go away for an extended period and you have other symptoms along this one, it may mean that throat cancer is present.
Unexplained Weight Loss:
Another symptom shared by many forms of the big C. If you experience unexplained weight loss, it’s best to get a check as soon as possible.
